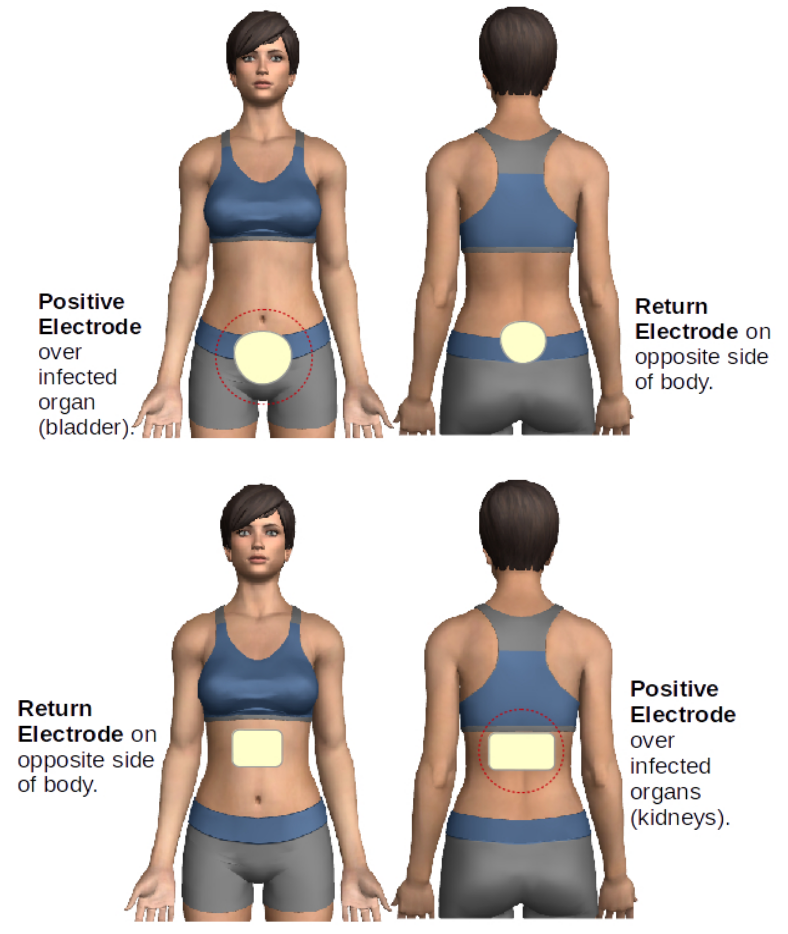
UTI & KIDNEY INFECTION TREATMENT
Infection:
Kidneys (pyelonephritis), ureters, bladder (cystitis) and urethra (urethritis). Can be upper UTI involving the kidneys, lower UTI or entire UTI. Sometimes called a "urine infection".
Type:
Mostly bacterial, less commonly viruses and other microorganisms, often Escherichia coli (E. coli).
Incidence:
Can be acute or chronic. Females have an approximately 3 × higher percentage of UTIs. More common in adults than in children. Millions of medical office visits per year even in developed countries.
Transmission:
From the large intestine and rectum if inadequate hygiene. Sexual intercourse can introduce the bacteria and viruses into the urinary tract.
Symptoms & effects:
Lower UTI: Inflammation leading to pain and burning during urination, sparse, frequent (night) and urgent urination, cloudy urine, plevic area pain, low grade fever, feeling unwell.
Upper UTI: Higher fever, nausea and vomiting, pain in lower back or sides of mid abdomen. Possible long term kidney damage and failure.
Drug treatment:
Oral and IV antibiotics.
Fluoroquinolone antibiotics can be used as last-line treatment, but global evidence from overuse is of growing superbug resistance. Resistance of multidrug-resistant (MDR) E. coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa is increasing. General efficacy of antibiotics is less, if infection contracted in some parts of the world, e.g., Southeast Asia, due to greater risk of MDR bacteria.
Side effects:
Multiple possible, mild (nausea) to severe, including long-term nerve damage (peripheral neuropathy).
SIS MACHINE TREATMENT
Bacterial infection: 2.5μA